
Maternal & Child Health Data
Breastfeeding, 2022
Breastfeeding can benefit child health and development and maternal well-being. Breastfed infants have lower risk of mortality, type 2 diabetes, and asthma than infants who are not breastfed. Breastfeeding can decrease mothers’ risks of ovarian and breast cancers, and help prevent postpartum depression. Not all mothers have equal access to breastfeeding supports, and structural racism can impede access to health care and breastfeeding information across racial and ethnic groups. The table below presents data disaggregated by race and ethnicity to help us identify inequities and work toward solutions that promote equity. Due to data limitations, data on this indicator cannot be disaggregated at the state level.
Home Visiting as Part of the Solution. Home visiting actively promotes breastfeeding, supporting mothers directly and connecting them to other services to encourage initiation of and sustained breastfeeding over time.
Breastfeeding by State, 2019 – 2020
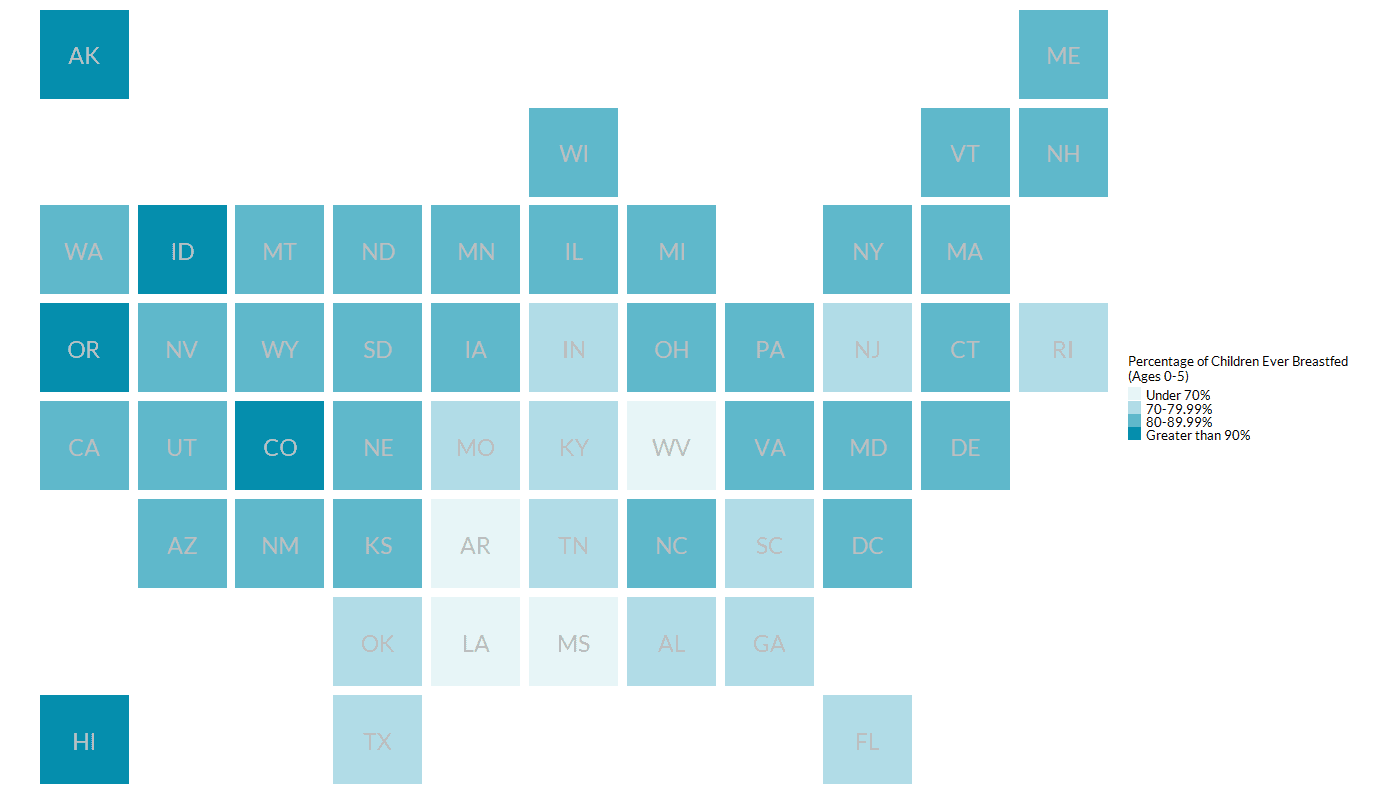
| State | All Groups | American Indian Alaska Native | Asian | Black or African American | Native Hawaiian Pacific Islander | Hispanic | Multiple Races | White |
Notes: NA indicates that the total number of respondents to this measure (unweighted denominator) is less than 30, which does not meet Maternal and Child Health Bureau data display criteria. Counts associated with specific racial and ethnic groups (that is, Asian, Black or African American, Hispanic, and White) are mutually exclusive. NA also indicates that data were not reported for American Indian/Alaska Native, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and Multiple Races.
Definition: Breastfeeding refers to the percentage of children ages 0-5 who were ever breastfed or fed breast milk. The full population sample, pooled from 2019-2020 (two years combined) data, includes non-institutionalized children in the United States aged 0–17 and is weighted to be representative of that subgroup of the U.S. population. Breastfeeding data included in previous Home Visiting Yearbooks was from the National Immunization Survey and defined as the percentage of infants born in a given year who were ever breastfed or fed breast milk, which was not available by race or ethnicity at the state level. This year, we include data from the National Survey of Children’s Health, which is available by race and ethnicity at the state level.
Sources: Child and Adolescent Health Measurement Initiative. 2019-2020 National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH) data query. Data Resource Center for Child and Adolescent Health supported by Cooperative Agreement U59MC27866 from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration’s Maternal and Child Health Bureau (HRSA MCHB). www.childhealthdata.org.