
Maternal & Child Health Data
Child Maltreatment (per 1,000), 2020
Child maltreatment and neglect occur all too frequently in the United States. In 2020, the rate of substantiated child maltreatment was 8.4 per 1,000 children under age 18, with infants under age 1 having the highest rate of victimization (25.1 per 1,000 children of the same age). Not all parents have equal access to parenting supports that can help prevent child maltreatment, and structural disinvestment in communities of color can drive disparities across racial and ethnic groups. The table below presents data disaggregated by race and ethnicity to help us identify inequities and work toward solutions that promote equity.
Home Visiting as Part of the Solution. Home visitors teach parents how to engage with their children in positive, nurturing, and responsive ways, and they educate them about child development and age-appropriate behavior. Such information and skills may help reduce instances of child maltreatment. By offering a supportive relationship to parents, home visiting also helps reduce parental stress, an important risk factor for child maltreatment. As a result, children whose parents participate in home visiting may experience less physical and psychological aggression than children whose parents do not participate.
Child Maltreatment by State (per 1,000), 2020
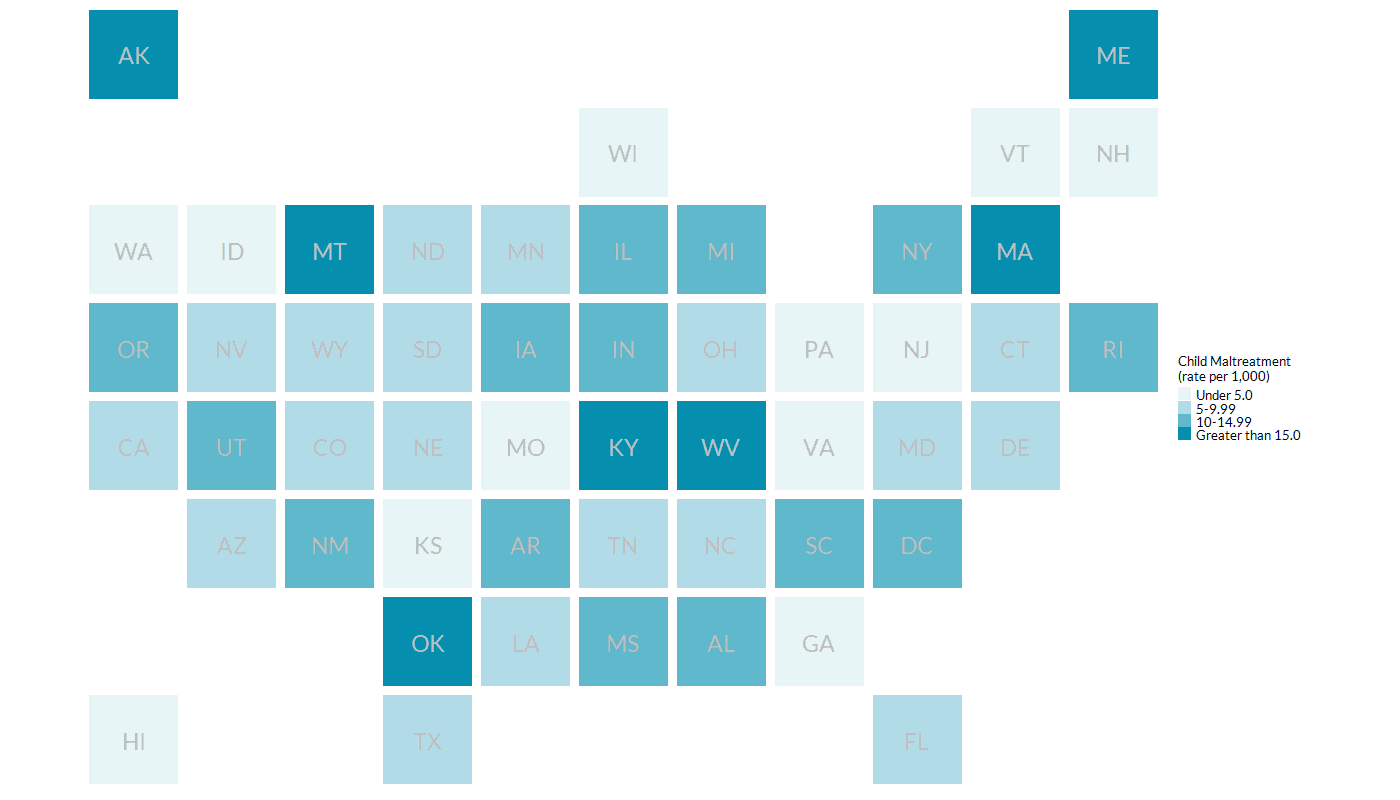
| State | Rate Per 1,000 Children | Rate per 1,000 American Indian or Alaska Native Children | Rate per 1,000 Asian Children | Rate per 1,000 Black or African American Children | Rate per 1,000 Hispanic Children | Rate per 1,000 Children of Multiple Races | Rate per 1,000 Pacific Islander Children | Rate per 1,000 White Children |
Notes: The multiple race category is defined as any combination of two or more race categories. Counts associated with specific racial groups (e.g., White) are exclusive and do not include Hispanic. NA appears in cells where data was not available.
Definition: Child maltreatment refers to the rate per 1,000 children aged 0–17 with substantiated reports of child abuse or neglect in 2020. In the National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System (NCANDS), a substantiated disposition is one that “concludes the allegation of maltreatment or risk of maltreatment was supported or founded by state law or policy.” A victim is defined as a child for whom the state determined at least one reported incidence of maltreatment was substantiated or indicated(Source: Indicated: A less commonly used investigation disposition that concludes maltreatment could not be substantiated under state law or policy, but there was reason to suspect that at least one child may have been maltreated or was at risk of maltreatment. This is applicable only to states that distinguish between substantiated and indicated dispositions.)Go to footnote #>1 or the child received a disposition of “alternative response” victim.(Source: Alternative response victim: The provision of a response other than an investigation that determines a child was a victim of maltreatment. Three states report children in this category, and it refers to those instances where the child protective services (CPS) agency or the courts required a family to receive services. Even though these children are considered victims by NCANDS, a perpetrator is not determined.)Go to footnote #>2 It is difficult to interpret differences in rates across states because each state has its own definitions of child abuse and neglect.
Source: U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. (2022). Child maltreatment 2020, table 3–3 child victims, 2016–2020; table 3–7 victims by race or ethnicity, 2020. https://www.acf.hhs.gov/cb/report/child-maltreatment-2019