There is no single data source about the recipients of evidence-based early childhood home visiting services. The NHVRC reached out to home visiting models considered evidence based in 2021 and to state, territory, the District of Columbia, and tribal Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting (MIECHV) Program awardees.
Their collective response moves us closer to depicting the hundreds of thousands of families working with evidence-based home visiting programs to pursue better lives. We recognize the information presented in the 2022 Home Visiting Yearbook likely undercounts the reach of home visiting services in 2021; still, we believe it presents the best nationwide look at home visiting services.
Fifteen evidence-based models operating across the United States in 2021 provided data on the number of families and/or children served.
According to the data received—
Of the more than 3 million home visits provided, at least—
Learn More About the National Landscape
Although the number of families served by evidence-based models is substantial, it represents only 1.6 percent of the more than 17.5 million pregnant caregivers and parenting families who could benefit from home visiting. The percentage of families served rises to 3.3 percent if one restricts the pool of potential beneficiaries to our estimate of high-priority families. (Source: The 3.3 percent estimate makes the simplifying assumption that the 277,852 families served are high-priority families.)Go to footnote #>1
Percentage of Families Served (2021)
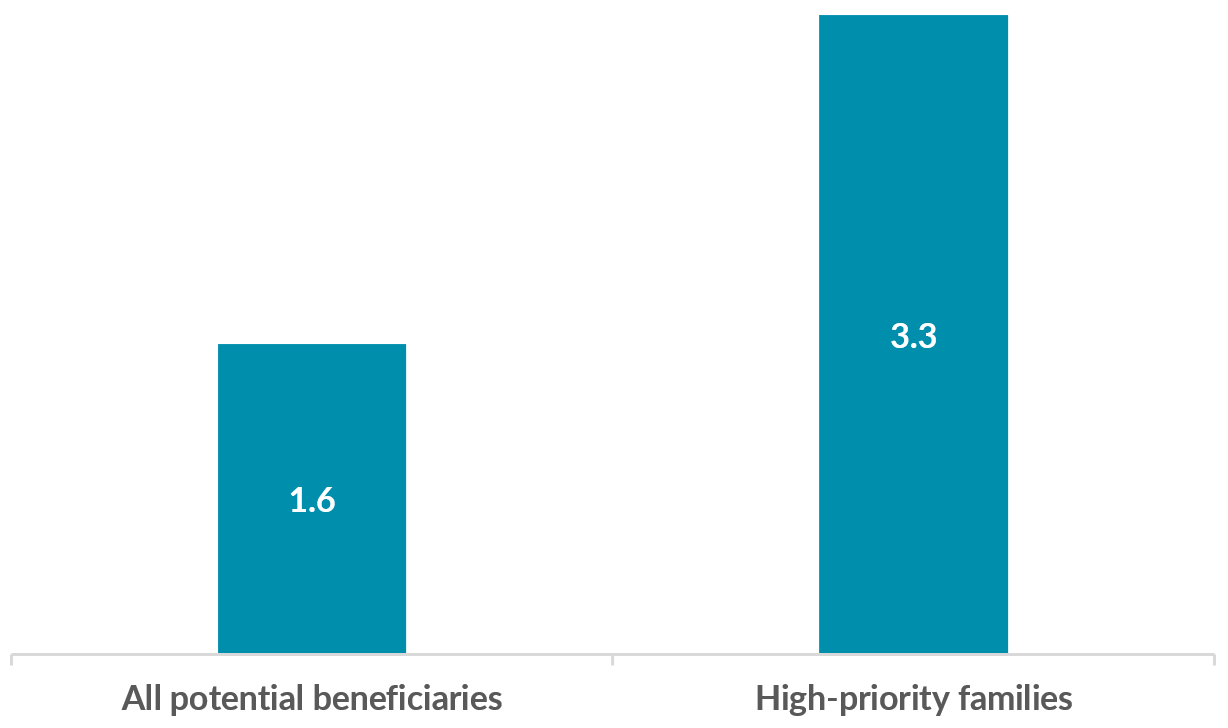
Source: Calculations based on data collected from 15 evidence-based models operating in the United States in 2021, and tabulations of the [American Community Survey](https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs/) (2016–2020).
What Do We Know About Other Home Visiting Models?
The Home Visiting Yearbook primarily shares data on home visiting provided by models designated as evidence based by the Home Visiting Evidence of Effectiveness (HomVEE) project. Since 2018, we have explored information about emerging home visiting models that demonstrate some evidence of effectiveness but have not been designated by HomVEE as evidence based.
Many emerging models are well established, and several meet some criteria of rigorous evidence. All play an important role in the home visiting landscape, often serving many families or being implemented across several locations.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to designating models as evidence based. Entities such as HomVEE, the National Registry of Evidence-based Programs and Practices, and state-level organizations use different—although sometimes overlapping—criteria to review a program’s effectiveness. For example, HomVEE looks at the type of study used to evaluate a model and study characteristics such as attrition and confounding factors.
Evidence builds along a continuum. Although the process may seem linear, various steps or iterations are often involved in moving forward along the continuum. Some emerging models will reach the final phase of the continuum with time. Others may not advance for various reasons. For example, rigorous evaluation takes time and money, and programs may not have enough personnel to conduct an experimental study.
Continuum of Evidence for Home Visiting Models

Sources:
FRIENDS National Resource Center. (n.d.). Evidence-based practice in CBCAP. [https://friendsnrc.org/evaluation-toolkit](https://friendsnrc.org/evaluation-toolkit)
Child Care and Early Education Research Connections. (n.d.). Child care & early education glossary. [https://www. researchconnections.org/childcare/childcare-glossary](https://www.researchconnections.org/childcare/childcare-glossary)
Philadelphia’s Department of Behavioral Health and Intellectual disAbility Services. (n.d.). Frequently asked questions: Evidence-based practices. [https://dbhids.org/epic/frequently-asked-questions#toggle-id-4](https://dbhids.org/epic/frequently-asked-questions#toggle-id-4)
Cooney, S. M., Huser, M., Small, S., & O’Connor, C. (2007). Evidence-based programs: An overview. What Works, Wisconsin Research to Practice Series 6. University of Wisconsin–Madison/Extension.

