Play and Learning Strategies
Play and Learning Strategies (PALS) works to strengthen the bond between parents and children using a responsive caregiving model. The model also provides stimulation that supports the development of children’s language, cognitive skills, and social development.
What is the model’s approach to providing home visiting services?
Home visits take place once per week for 60 to 90 minutes. Services are provided until the curriculum is completed, which takes 10 weeks for infants and 12 weeks for toddlers and preschool-age children. PALS requires families to initiate services following the birth of the child. Families may enroll when the child is between 5 and 59 months old, although the model recommends that families enroll before the child is 4 years old.
PALS’ service population includes the following:
- Caregivers under 21 years old
- Caregivers who are unmarried or single
- Caregivers with limited access to education
- Children with developmental delays or disabilities
- Families with a history of child abuse or neglect/involvement with child welfare system
Who is implementing the model?
Home Visitors
PALS was implemented by 6 home visitors in 2020. The model requires an associate’s degree in early childhood or work experience commensurate with education and a high school diploma for home visitors; a bachelor’s degree is recommended. The maximum caseload requirement for home visitors is 15 families.
Supervisors
PALS was implemented by 3 supervisors in 2020. The model requires a bachelor’s degree for supervisors; a master’s degree is recommended.
Where is the model implemented?
PALS operated in 3 local agencies across 3 states in 2020.
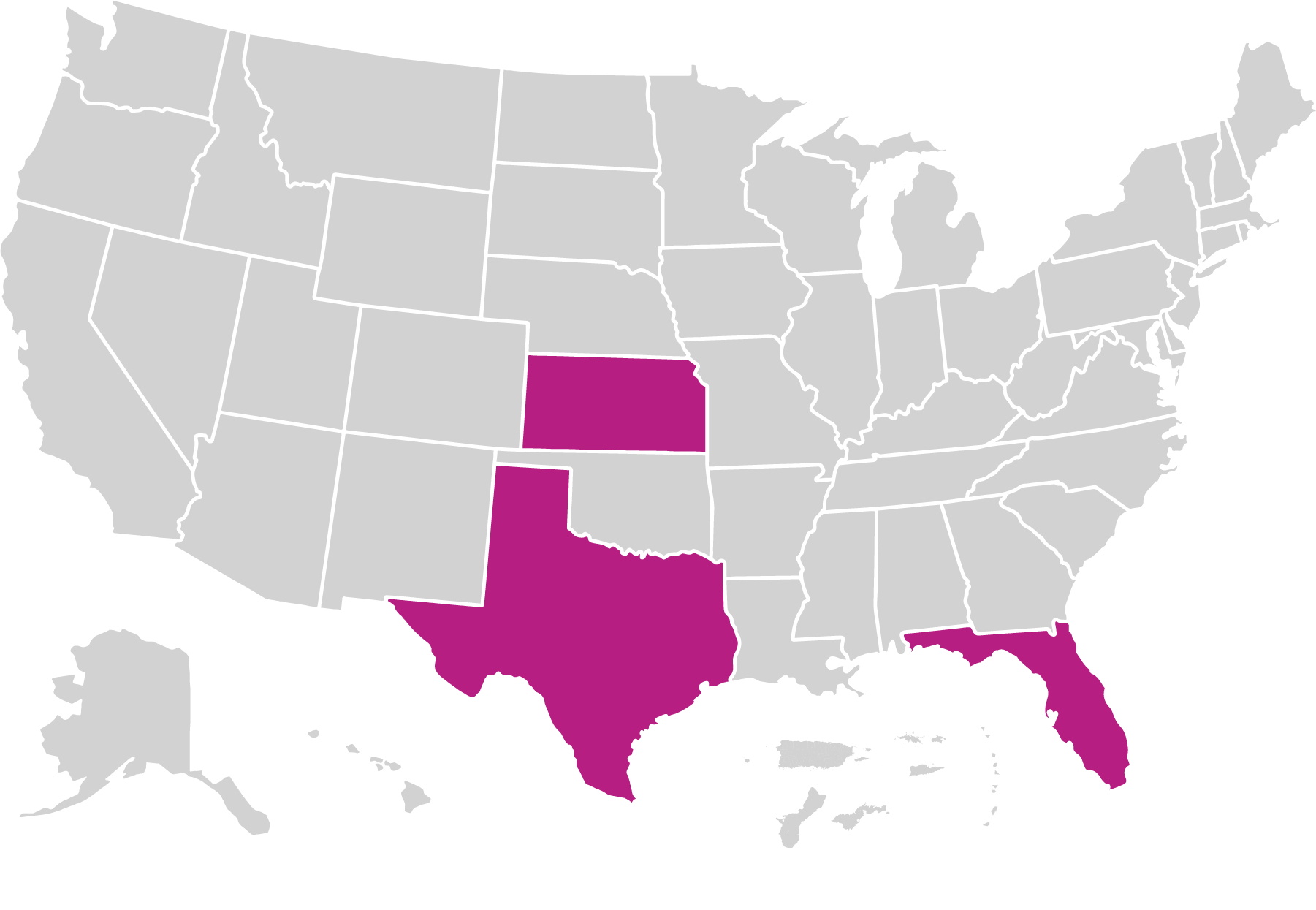
Families Served Through Evidence-Based Home Visiting in 2020
Mission
PALS helps parents master specific skills for interacting with their infants, toddlers, and preschoolers to lead to better child outcomes. PALS has a particular focus on supporting children from families with limited resources. PALS educates parents about typical behaviors to expect from children at different ages so that parents can support the healthy development of their young children.
History
The original PALS curriculum was developed based on longitudinal research conducted by Susan Landry, Ph.D., Karen Smith, Ph.D., and their colleagues on the development of premature and full-term infants over time. The families were followed over 15 years, during which researchers identified key parenting behaviors that predicted better child outcomes. The basis for the PALS curriculum was formed around teaching the following key skills: contingent responsiveness, emotional/affective support, support for children’s focus of attention, and rich language stimulation. Today, multiple research studies provide evidence that PALS positively impacts participating families and children.